How to Build a Verifier: A Short Survey
目录
Preface
As is well known, verifiers play a crucial role in at least two scenarios. First, in agent architectures, a stop condition is required to exit the loop. Second, in RLVR (Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards) architectures, a verifier is needed to determine rewards within the RL environment.
Thus, in this blog post, I present a survey of verifiers in the LLM era.
Industry
The overall process is illustrated below:
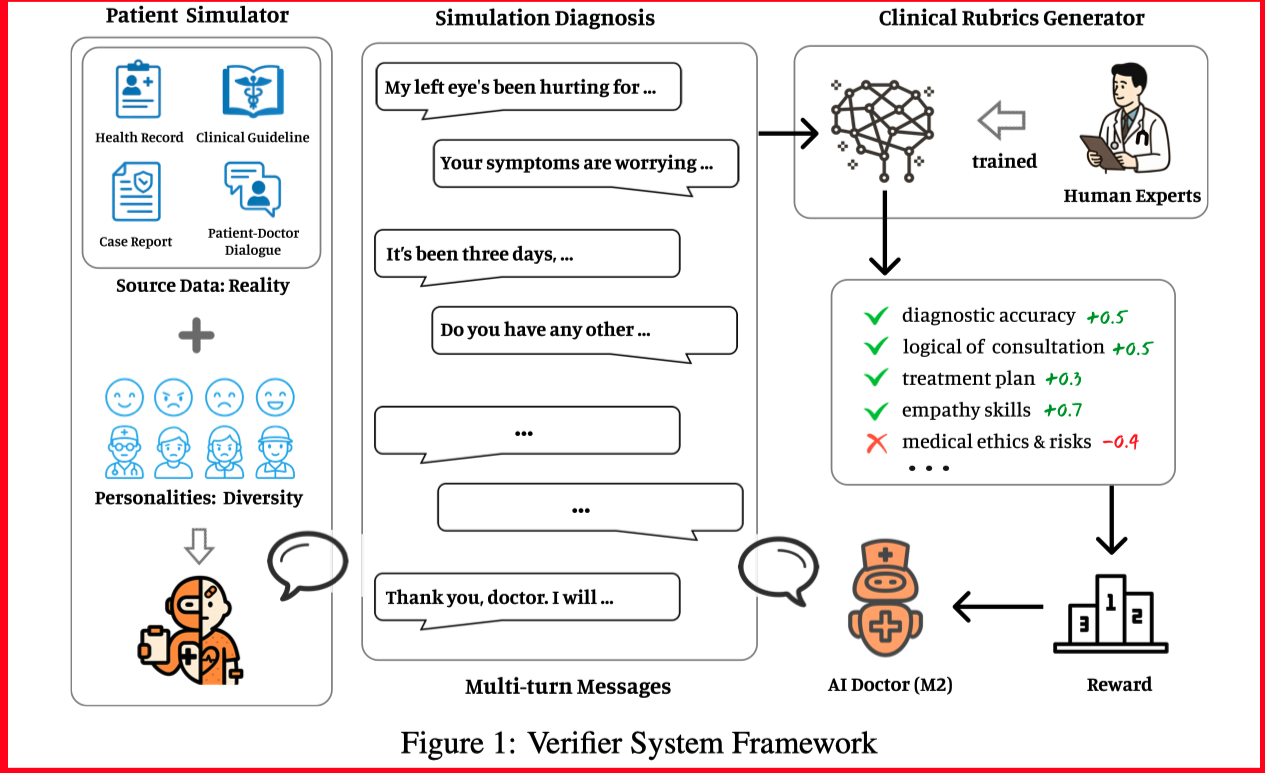
The most interesting component is the Clinical Rubrics Generator, which consists of three parts:
-
Prompt Collection and Processing
This work constructs prompts from three major sources: medical record-driven prompts, knowledge base-driven prompts, and synthetic scenario prompts.
-
Rubric Collection
Based on the aforementioned prompts, LLMs are utilized for rubric construction to derive actionable quantitative metrics.
-
Training of Rubrics Generator
After training, the Rubrics Generator can produce dynamic evaluation standards in real-time, providing AI physicians with continuous, reliable feedback while effectively managing computational costs.
-
QuarkMed Medical Foundation Model Technical Report
In this work, a General Verifier is trained as an instruction-following model. By providing it with explicit evaluation principles, the model can score responses based on their adherence to these rules.
Academia
-
Compass Verifier: A Unified and Robust Verifier for LLMs Evaluation and Outcome Reward
The contributions of this paper are two-fold: VerifierBench (a benchmark) and CompassVerifier (a learnable model).
The VerifierBench pipeline consists of three stages:
- Stage 1: Multi-expert voting
- Stage 2: Multi-prompt voting
- Stage 3: Annotation and analysis
To obtain the model, CompassVerifier employs three data augmentation methods, including complex formula augmentation and error-driven adversarial augmentation. Furthermore, generalizability augmentation is applied to enhance data diversity. A training sample is structured as follows:
[Question, Response, GT]
This model is compared with xVerify. Both methods suggest that a learnable verifier is plausible.
-
xVerify: Efficient Answer Verifier for Reasoning Model Evaluations
This work is similar to the one above, sharing the emphasis on the importance of data augmentation. Ultimately, this method yields a 0.5B model that outperforms other methods.
-
CompassJudger-2: Towards Generalist Judge Model via Verifiable Rewards
This work follows a similar paradigm to the aforementioned studies.
-
EasyJudge: An Easy-to-use Tool for Comprehensive Response Evaluation of LLMs
This work is based on pointwise and pairwise evaluation methods.
-
Generative Judge For Evaluating Alignment
Similar to the works above, this paper focuses on generality, flexibility, and interpretability.
-
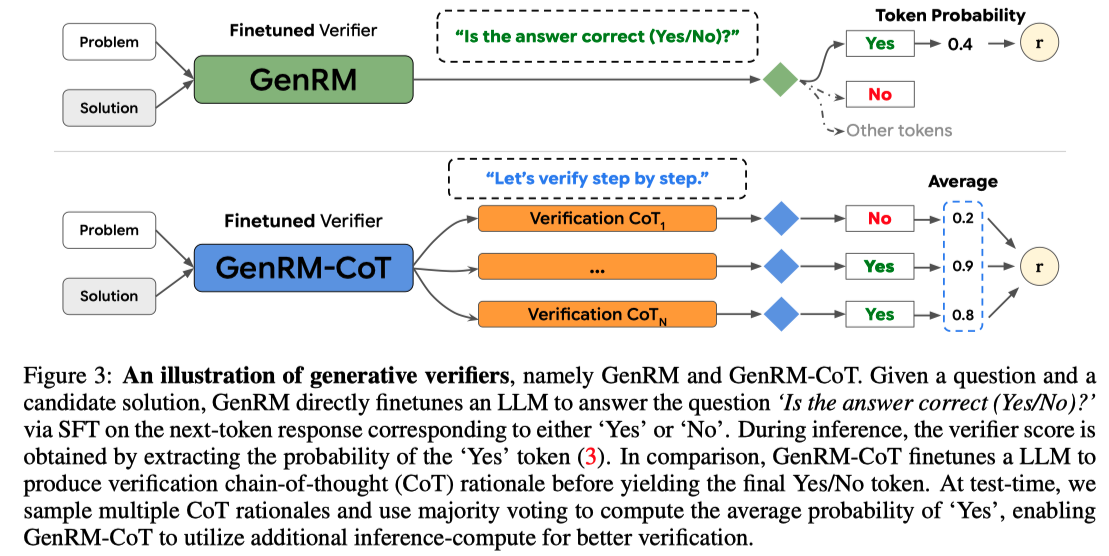
Generative Verifiers: Reward Modeling As Next-Token Prediction (ICLR 2025)
This paper differs from other works. While LLM-based verifiers are typically trained as discriminative classifiers, this paper trains a generative model with a next-token prediction objective.
-
JudgeLM: Fine-Tuned Large Language Models Are Scalable Judges
This work follows a similar paradigm.
-
M-Prometheus: A Suite of Open Multilingual LLM Judges
As a branch of “LLM-as-a-Judge,” this paper trains a multilingual model using a learning paradigm similar to the works mentioned above.
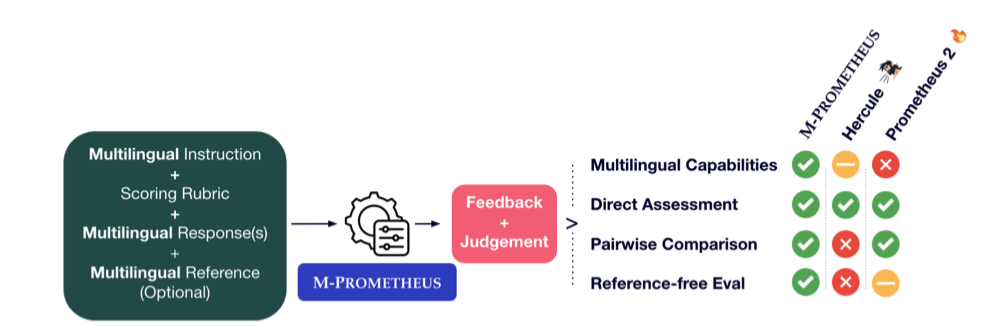
This paper is related to “PROMETHEUS: INDUCING FINE-GRAINED EVALUATION CAPABILITY IN LANGUAGE MODELS.” The interesting part is “score rubric mining,” a method similar to one found in Baichuan-M2.
-
PandaLM: An Automatic Evaluation Benchmark for LLM Instruction Tuning Optimization
Similar to the above, a training example for PandaLM is as follows:

The prompt used for training PandaLM is as follows:

Conclusion
Finally, we need to consider the following idea: Can we build a general evaluator? Is an evaluation rubric necessary in the evaluation process?
Related Materials
-
VERIF: Verification Engineering for Reinforcement Learning in Instruction Following
-
Variation in Verification: Understanding Verification Dynamics in Large Language Models
-
Trust, But Verify: A Self-Verification Approach to Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards
-
From DeepSeek V3 to V3.2: Architecture, Sparse Attention, and RL Updates
this blog talked more about verifier in DeepSeekMath, certainly including meta-verfier.
扫码加笔者好友,茶已备好,等你来聊~